How Does Screen Time Impact the Brain? A Detailed Explanation
In today’s digital world, screens have become an essential part of everyday life. From smartphones and laptops to televisions and tablets, people spend several hours each day interacting with digital devices. While technology offers countless benefits—convenience, communication, information, and entertainment—it also raises a growing concern: how does excessive screen time affect the brain?
This detailed guide explores how screen exposure changes brain structure, affects mental health, influences children’s development, impacts adults’ cognitive performance, and what you can do to maintain a healthy digital lifestyle. If you are experiencing symptoms such as poor concentration, headaches, mood swings, sleep disturbances, or memory problems, consulting a brain specialist in Pune can help in early detection and guidance.
Understanding Screen Time: Why It Matters More Than Ever
Screen time refers to the total amount of time spent using devices such as:
- Smartphones
- Computers and laptops
- Tablets
- Televisions
- Video games
- Virtual reality devices
According to recent global studies, adults spend 7–9 hours per day in front of screens, while teenagers may spend more than 10 hours daily. This high exposure significantly influences how the brain functions, processes information, and manages stress.
Screens stimulate the brain differently from real-world interactions. Digital stimuli are fast, colorful, and highly engaging. Over time, this rewires the brain’s reward pathways and affects attention, memory, emotional balance, and sleep cycles.
How Screen Time Affects Brain Structure and Function
Research in neuroscience shows that prolonged screen exposure can influence both the structure and function of the brain. Here are the primary areas affected:
Impact on Attention Span and Cognitive Control
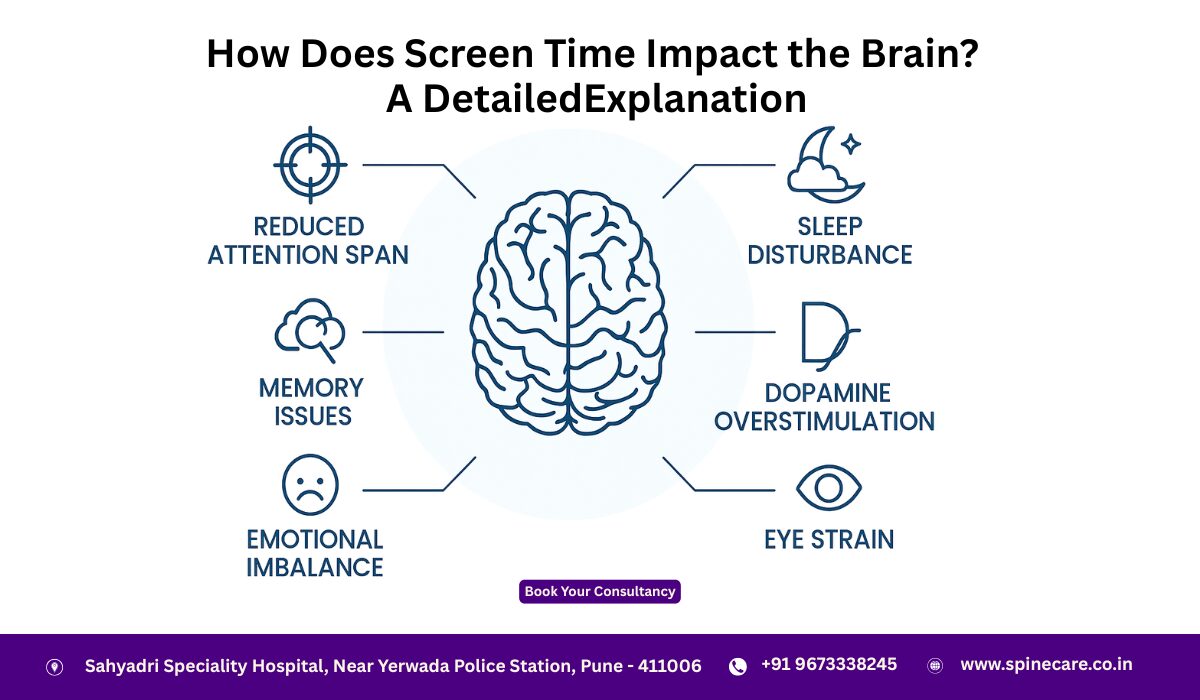
Frequent switching between apps, notifications, and multitasking trains the brain to constantly shift focus. This reduces deep concentration and increases cognitive fatigue.
Key effects:
- Reduced attention span
- Difficulty focusing on one task
- Increased distractibility
- Lower productivity
Studies show that digital multitasking weakens the prefrontal cortex—the part of the brain responsible for planning, decision-making, and impulse control.
Effects on Memory and Learning Ability
Screens often provide information rapidly, which may reduce the brain’s ability to store information deeply.
How it affects memory:
- Lower retention of information
- Reduced ability to store long-term memories
- Dependency on digital reminders instead of internal memory
This is especially concerning in children, whose brains are still developing.
Changes in the Brain’s Reward System
Apps, games, and social media platforms are designed to activate dopamine—the neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward.
Excessive screen time can lead to:
- Dopamine overstimulation
- Reduced ability to feel satisfaction from offline activities
- Addictive behaviors
- Constant craving for digital stimulation
This pattern resembles the neural activity seen in other forms of behavioral addiction.
Impact on Emotional Regulation
Too much screen exposure affects areas responsible for emotional processing.
Possible outcomes include:
- Increased irritability
- Mood swings
- Emotional numbness
- Difficulty handling stress
- Reduced empathy
Children exposed to excessive screens often struggle with emotional self-control and frustration management.
Screen Time and Mental Health
Excessive digital exposure is strongly linked to several mental health concerns. Understanding these effects is crucial for prevention.
Anxiety and Stress Disorders
Constant connectivity keeps the brain in a state of alertness. Notifications, social comparison, and information overload increase stress hormones such as cortisol.
Signs of screen-induced anxiety:
- Restlessness
- Irritation when away from the phone
- Fear of missing out
- Social anxiety
- Overthinking and mental exhaustion
Gamers, social media users, and working professionals are especially vulnerable.
Depression and Emotional Burnout
Overuse of digital platforms affects mood regulation pathways in the brain. Excessive exposure to negative news, comparison with others, or online bullying contributes to depressive symptoms.
Effects include:
- Lack of motivation
- Emotional fatigue
- Withdrawal from real-life activities
- Hopelessness or low mood
If these symptoms persist, consulting a brain specialist in Pune is recommended for early intervention.
Impact on Sleep: Blue Light and Melatonin Disruption
Blue light emitted from screens interferes with the brain’s circadian rhythm.
Effects of nighttime screen use:
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Light or disturbed sleep
- Reduced REM sleep
- Daytime fatigue
- Reduced brain performance
Poor sleep affects memory, learning, emotional balance, and overall brain health.
Impact of Screen Time on Children’s Brain Development
Children’s brains develop rapidly, making them more sensitive to screen exposure.
Delayed Language and Communication Skills
Children who spend excessive time on screens often have limited face-to-face interaction, which is critical for language development.
Possible outcomes:
- Delayed speech
- Poor vocabulary
- Difficulty expressing thoughts
- Reduced social communication skills
Impaired Social Skills and Real-World Interaction
Screen-dependent children often show:
- Poor eye contact
- Difficulty engaging in group activities
- Reduced empathy
- Increased behavioral issues
They may struggle to read facial expressions or understand emotional cues.
Hyperactivity and Behavioral Issues
Fast-paced videos and games stimulate the brain excessively, contributing to attention and behavior problems such as:
- Hyperactivity
- Impulsiveness
- Poor frustration tolerance
- Aggressive behavior
Parents should monitor screen time closely, especially in early childhood.
Impact of Screen Time on Adults’ Brain Health and Productivity
Adults often rely on screens for work, entertainment, and communication. This has unique effects on the adult brain.
Digital Eye Strain and Headaches
Extended screen time can cause:
- Eye dryness
- Blurry vision
- Headaches
- Neck and shoulder pain
These symptoms negatively impact concentration and work productivity.
Reduced Cognitive Performance
People who spend many hours on screens often experience:
- Mental fatigue
- Slower information processing
- Reduced creativity
- Lower problem-solving abilities
This happens because the brain rarely gets downtime from constant stimuli.
Emotional Exhaustion and Burnout
Virtual meetings, long work hours, and online multitasking contribute to digital burnout.
Symptoms include:
- Irritability
- Loss of interest in work
- Chronic fatigue
- Reduced motivation
The Relationship Between Screen Time, Addiction, and the Brain
Screen addiction is becoming increasingly common. It occurs when the brain becomes dependent on digital stimulation to feel normal.
Signs of screen addiction:
- Spending hours online without realizing
- Neglecting responsibilities
- Irritation when interrupted
- Craving constant digital engagement
- Difficulty staying offline
Addiction patterns strongly affect reward circuitry in the brain, similar to other compulsive behaviors.
How Much Screen Time Is Considered Healthy?
While screen time cannot be eliminated, it can be managed wisely.
Recommended limits:
- Adults: Aim for less than 2 hours of recreational screen time daily
- Teenagers: Less than 3 hours per day
- Children (2–12 years): 1 hour per day
- Children below 2 years: Avoid screen time, except video calls
Tips to Reduce the Negative Impact of Screen Time on the Brain
Here are science-backed strategies to protect your brain health:
Follow the 20-20-20 Rule
Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
This reduces eye strain and mental fatigue.
Limit Blue Light Exposure at Night
- Reduce screen time 2 hours before bedtime
- Enable night mode
- Use blue-light filtering glasses if necessary
Practice Digital Detox
Choose specific days or hours when you stay away from screens completely.
Schedule Screen-Free Activities
- Reading
- Exercise
- Outdoor activities
- Mindfulness meditation
These activities help rebalance neurotransmitter levels.
Avoid Multitasking
Focus on one task at a time to improve attention span and productivity.
Create Tech-Free Zones
- Dining area
- Bedroom
- Study zone
This helps maintain mental boundaries.
Encourage Mindful Screen Use in Children
- Monitor content
- Limit device access
- Engage them in real-world activities
- Promote outdoor play
8. When Should You Seek Medical Help?
If you notice symptoms such as:
- Persistent headaches
- Trouble concentrating
- Memory problems
- Sleep issues
- Mood changes
- Anxiety or depressive symptoms
- Screen dependence
Then it is advisable to consult a neurological expert. A timely evaluation helps prevent long-term complications.
Conclusion
Screen time has become an unavoidable part of modern life. While technology provides convenience and productivity, excessive screen exposure can significantly impact brain health. It affects attention, memory, emotional regulation, sleep patterns, and cognitive performance. Children and adults both face risks, but with mindful usage, the negative consequences can be reduced.
Maintaining a balanced digital lifestyle, setting boundaries, practicing eye and mental breaks, and prioritizing real-world interactions can protect the brain from overstimulation. If symptoms persist or interfere with daily functioning, consulting a specialist is important.
A qualified brain specialist in Pune can help diagnose screen-time–related issues and provide appropriate guidance or treatment to restore optimal brain function.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does screen time affect the brain?
Excessive screen time impacts attention, memory, emotional balance, and sleep cycles due to overstimulation and blue light exposure. - Can too much screen time cause anxiety or stress?
Yes. Constant notifications, information overload, and digital dependency can increase stress hormones and trigger anxiety. - Does screen time affect children more than adults?
Yes. Children’s developing brains are more sensitive, leading to delayed speech, poor social skills, and behavioral issues if exposed to screens for long hours. - How much screen time is considered healthy?
Adults should keep recreational screen time under 2 hours daily. Children (2–12 years) should limit it to 1 hour, while toddlers under 2 years should avoid screens. - Does screen time disturb sleep?
Yes. Blue light suppresses melatonin and disrupts sleep patterns, causing insomnia and poor-quality sleep. - How can I reduce screen time effects on my brain?
Follow the 20-20-20 rule, use night mode, take regular breaks, avoid multitasking, and create tech-free zones at home. - When should I consult a specialist?
If you experience headaches, poor focus, sleep issues, mood changes, or screen addiction symptoms, seek guidance from a neurological expert or a brain specialist in Pune.




